SEO is short for “Search Engine Optimization”, which is the on-going process of improving the visibility and ranking of a website or web page in the organic search engine results presented in Google and other search engines.
A complex algorithm determines how search engines list the results for any given search term or phrase. Though the exact algorithm is a very well guarded secret, many of the important aspects and components of this algorithm are known; these are the components SEO focuses on.
Due to the complexity of Google, Yahoo, or Bing algorithms, and also because of the endless sea of websites and web content on the internet, SEO is a long-term effort.
How long the process takes to reach consistent visibility in search results is determined by the methods, strategies, priorities and ongoing efforts that are executed.
The following provides an outline and explanation of the basic components and strategies essential for successful SEO. From the outset, you must understand that SEO is constantly changing and evolving, just as search engines keep changing their algorithms, making them smarter and faster. One needs to understand how SEO worked in the past and how it’s working now, to determine how it would work in the future.
In this guide we are going to review the following:
- Modern day SEO vs. SEO in the past (2019-2023)
- How does Google SEO work
- Indexing and Site Maps
- On-site SEO elements
- Off-site SEO elements
- Step by Step SEO Basics
Why Does SEO Still Matter in 2023? And Why Is It More Important Than Ever?
Modern day SEO vs. SEO Marketing in the past
In the past, optimizing your website for search engines meant optimizing for the algorithm and the search bots. This was a mostly technical process that focused solely on link building and the way your website was structured. This left the door open for people to try and manipulate the system with techniques that now we consider to be spam. Google addressed that issue when it released the Panda and Penguin updates. These updates penalized websites with thin “spammy” content and websites who used link building strategies that were not organic and relevant to the content of the site, but instead designed to manipulate the search algorithm.
Today, optimizing your website for search engines means optimizing for the users you want to find your website (in other words, your target audience). The main focus of modern SEO is providing your target audience with the best content and user experience possible. Google wants to provide it’s users with the best results to match their search queries. By providing the best content to address those search queries, you increase your chances of ranking highly in the SERP (Search Engine Results Page).
That said, technical SEO is still important to ensure Google bots can understand the content on your page and index them correctly. If you are trying to rank for competitive keywords, high-quality content might not be enough and certain steps need to be taken in order to improve your domain authority, we will expand on this shortly but first, let’s start with the basics:
How does Google SEO work in 2023?
To understand how SEO works, one needs to first learn how a Google Search Query is executed. The below image is directly taken from the Google’s corporate site.
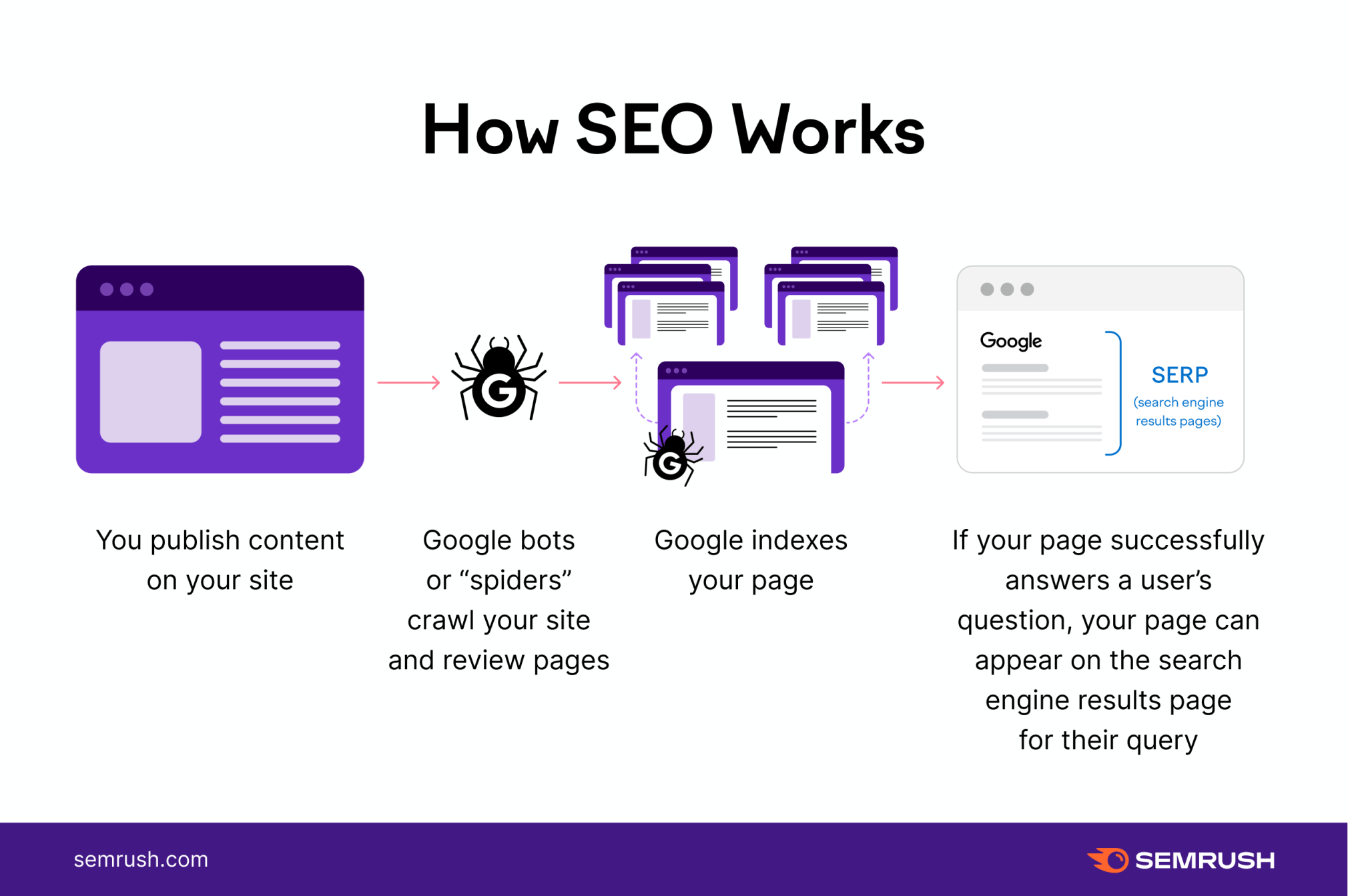
As you can see, everything goes through the Google servers as Google finds the most relevant indexed content based on the search term (query) and then displays it to the user.
Indexing and Site Maps
Google is the largest system of indexed content ever developed. To be included in the index, Google has to first know about and catalog your website, blog or other web pages. Designing and publishing a website does not mean it will automatically pop up on Google.
Google has to index your site in order for it to be crawled and ranked in search results. It’s like adding a new song to your music library so it’s a permanent component; or adding a business to the yellow pages. In order for your website to be found in a search, it has to be included in the “listings.” Regardless of the technology used to build your website, you want Google to be able to easily and correctly index your pages. If Google is unable to index your website you will not appear in search results.
The simplest way to have Google index your site is by manually submitting a sitemap to Google Search Console (formerly known as Google Webmaster Central). Bing has a similar platform called Bing Webmaster Tools. The sitemap provides search engines with the structure of a webpage.
How do you get Google to index your site?
- Ensure your website is crawlable, with regular server response, and content that crawlers understand (something as simple as a misplaced character in the robots.txt file of your website can block all bots from crawling your website).
- Verify your account with Google Search Console. There are multiple ways to verify your website, follow the instruction carefully and you should have no problem to get instant access to all the tools Google offers webmasters.
- Submit your sitemap. Both Google and Bing offer testing tools to check if your sitemap is set up correctly and nothing is blocking the bots from crawling the website, make use of this option and avoid frustrations later on.
Again, none of the above will guarantee overnight indexing by Google, but it will definitely help to decrease the time it takes. According to Google, websites can take anywhere from a couple days to a month to be searchable on Google, but more often than not, websites show up in search result pages within a week.
The Elements of On-Site SEO
On-site SEO refers to optimizing the website from within, using the aforementioned components as well as content, targeted words that are written strategically as well as other elements. Off-site SEO refers to the efforts made outside of the website, which will be discussed a little later. Below are some of the most important elements of on-site SEO:
Page Titles
Page titles are usually seen at the very top of an internet browser or in the window label or tab of an open web page. Another way to find out the title of a web page is to save it to favorites. Pages are saved according to their page titles. It is important to title all web pages using key terms that you want users to find your site with, and should match the key terms found in your written website content as well.
A mistake often made by business websites is to put their business name, logo or other material on these page titles. However, that will not help users find your site. For example, if a costume rental business by the name of “Monster Deals” has a page with female witch costumes, and would like to be found in a search by a similar search phrase, then the page title should be something close to “Women’s Witch Costumes.” Think of these terms according to how you would search for them – not according to what sounds or looks best.
Meta Descriptions
Meta description are displayed on the search results page, under the page title.
Those descriptions are implemented in the HTML code side of the website, at the head section of the page. Most Content Management System (CMS) allow you to add meta description without the need to manually edit the HTML code.
A good meta description should give an accurate and easy to understand description of the content of the page. You should include the keyword you are targeting but in an organic way so the description stays readable and grammatically correct. Technically, the length of a meta description is not limited by characters but Google truncates the description after approximately 300 characters (as of December 2017).
In the past, search engine used to give importance to another meta field called keywords, but nowadays it is best practice to leave that field empty.

Valuable, Worthwhile Content
Filling up your pages with fluff and self-promotional clichés may be the stuff of TV commercials and print advertisement but is not useful for search engine or human consumption. If your website content is unoriginal, auto-generated, “spun” (taking the same article and having it rewritten to basically say the same things with a few minor changes) or otherwise devoid of real value – not only will it not do well in search results, your website might also be penalized by search engines. Useful, original, well-written content is becoming a more and more critical component of a web page and a website as a whole.
There are several reasons for this.
- Original content, with chosen keywords used naturally and modestly, is given higher value in search results. As mentioned before, search engines give low rankings to sites that try to cheat with the overuse of keywords, also known as keyword stuffing.
- Worthwhile, updated and regularly added content is also another SEO strategy. Websites that regularly update and add good content to their site will rank higher in search results than old, stale content that has not been revisited or updated by the writer.
- The more informational, useful, well-written and otherwise valuable content a website has, the more opportunities to receive inbound links from other sites, which is an extremely important ranking factor.
- The more content a website has, the more opportunity for deep links – which are widely accepted as one of the most important factor in SEO. Deep links are backlinks that link to internal sections, subsections of your website. It serves to prove to Google et al that specific and targeted information has been found, read and linked to by another site that finds this content valuable.
If you own a business, or are monetizing a blog, then obviously you have expert information about a particular subject. The more valuable content you provide your visitors, the better it is for your website. Essentially, you must put your audience ahead of conversion rates, sales, or other typical business priorities.
Your sales and other business goals must result from offering expertise, valuable information and insight; not from content that is “sales forward”. This really works both for the search engines and your targeted audience.
Technical aspects of Onsite SEO (How do you do SEO for a website?)
While having rich, valuable, original content is now the most important factor of onsite SEO, there are still several elements that are more technical but still very important.
- Internal and external links – Having a good internal linking structure helps users navigate your site and helps search bots to understand the hierarchy of the pages on your website. Having a few external links (links leading to a different domain) can be a good thing as well. For example within the content of a blog post. That said, it is important that those links be relevant to the content of the page. It is also important to not add too many external links on your website as that might be perceived by search engines as spam.
- Page Load Speed – The faster it takes for a page on your website to load, the better. A fast website provides a better user experience, decreases the bounce rate and can ultimately result in increased ranking. Google offers the PageSpeed Insights tool to check the speed of your website and offers suggestions on how to improve it. One of the Google updates in 2018 has to do with website speed. Up until 2018, the speed of a website was determined by the response time measured by the Google bots. Meaning, the bots measured the time it took for a page to load and that was used as the indicator of a website’s speed. The problem with that is that different devices, servers and connection speeds might have different response times. To address this, Google is now relying more heavily on Google Chrome users and how long it takes for a website to load on their end.
- Mobile Friendliness – More than half of Google searches are performed on smartphones and tablets. If your site is not mobile friendly, Google is less likely to show your website in a result page on those devices. This means you might be missing out on ~60% of all search engine users. Mobile friendliness is also known as responsive web design.
- Content Management Systems (CMS) – The CMS you use to create and upload content definitely matters to SEO. Aspects to look out for include clean, search engine friendly URLs, ease of content creation and caching, metadata forms, and whether the CMS is optimized for your particular kind of website. For example, WordPress is a great SEO friendly CMS, but it is not ideal for eCommerce sites, or at least not for sites that sell a lot of products. A good CMS system will also take all the factors we mentioned above into consideration (mobile friendliness, speed, and site structure).
Off-Site SEO and How it Works
Offsite SEO is a general term for all actions and strategies taken to improve a website domain authority and visibility beyond the website itself. The biggest difference between on-site SEO and off-site SEO is that the former can be completely controlled by the webmaster and/or content manager of a website and the latter cannot be totally controlled. That said, the success of any offsite technique or process is driven by the quality of the content (which you can control), whether it be an article, press release, blog post, video etc.
The key element of off-site SEO is Backlinks. Backlinks are links on other websites that are leading back to your website. In the past, new websites could simply purchase backlinks and instantly see an improvement in search ranking. Today, these practices are considered “black hat SEO” and Google not only frowns upon them but might actually penalize your website. However, backlinks are still considered to be one of the most important factors in Google’s search algorithm. Let’s review some of the different types of backlinks.
- Organic backlink – When a website links back to your site without any outreach taken by your part. This can happen when you offer high-quality content that people will want to reference in their websites and blogs.
- Brand Mentions – A backlink to your homepage using your brand name as the anchor text is very common when you get backlinks via media mentions, guest blogs, press releases, etc.
- Deep Backlinks – A link to your website that does not lead to your homepage but instead one of the inner pages of your website. A lot of time these links have anchor texts such as: “learn more”, “click here”, etc. If you can control the anchor text used in these backlinks, it is much better to use the keyword you want to target for that specific page (assuming that the content on that page is truly relevant to that keyword). For example, instead of: “Click here to learn more about competitive backlink analysis” use this: “Learn more about competitive backlink analysis”
- Placed Backlinks – These are links on websites that allow user-generated content. For example: Social media, comment section in blogs, forums, etc. These links don’t necessarily carry as much weight as the other types of backlinks mentioned above.
Not All Backlinks Are the Same
Backlinks carry different weight in Google’s eyes, depending on these factors:
- Domain Authority (DA) and Page Authority (PA) – Backlinks from website with high DA are much more valuable than backlinks from websites with low or average DA. Another factor is PA. A new page on a website will have no PA, even if a website has high DA. The higher the DA and PA are, the better.
- Relevance – You want the websites linking back to your website to be relevant to your industry and target audience. If you have a lot of links coming from website that are completely unrelated in content to your website, that might raise a red flag.
- Spammy Websites – If a website is considered to be spammy in Google’s eye then a backlink from that website might actually hurt your SEO. A spammy website is typically a website with thin to no content, a lot of external links and a lot of ads.
- NOFOLLOW Links – “nofollow” is an attribute that can be added to an <a> tag (a link tag in html). This attribute tells search engines to not follow that link to the destination website. These links are generally considered less valuable than “follow” links.
SEO (Search Engine Optimization) Pricing
The prices for SEO services vary based on the location of the client and the in-depth execution of the project. For example, a local SEO project (for a local business) is very different in scope than a project that aims to improve ranking nationally or globally. Another difference is the type of package.
Most common SEO packages are: monthly, one time project and consultative.
- One time project– Typically focuses on the technical aspects of onsite SEO. Deliverables can include updating page titles and description, page content, site structure, site speed and more.
- Consultation – Typically billed on an hourly basis with prices based on the consultant’s record and experience. An SEO consultation offers guidance, strategy and expertise but usually very little hands-on changes to the website.
- Monthly– The most effective package is a monthly ongoing strategy that is based on adapting to search trends and the consistent algorithm changes made by search engines.
Here are a few price ranges based on the type of client and the nature of the project:
eCommerce SEO
Optimizing an eCommerce website for search engines requires a unique strategy and special attention to details. This is due to the fact that it is quite difficult to get a product page to rank organically. An eCommerce SEO package will typically include content creation, monthly keyword research, onsite optimizations and a backlinking strategy. Prices range from $3,000 to $20,000 per month, depending on the size of the website (amount of products) and the specific deliverables.
Lead Generation SEO
Websites for SAAS companies or companies providing any type of service are geared towards generating leads. On one hand, these websites tend to be significantly smaller than eCommerce websites. On the other hand, they rely heavily on great content in order to stand out. There are also different SEO strategies for B2B and B2C leads. An SEO package for a SAAS company or other service provider will include an extensive content marketing plan, and a comprehensive backlinking strategy as well as onsite optimizations. Prices range from $3,500-$15,000 per month depending on the scope of work.
Local SEO
Search results change based on your location, especially when searching for a service that is location based. For example, if you are in Miami and you search for “flower delivery” you will see local businesses relevant to the Miami area. If you search that exact same term in New York City, you will see completely different results. A local SEO package will typically include onsite optimizations, content marketing that is focused on the service area, optimizing business listings (on Google, Yelp, etc.) and implementing tactics to increase customer reviews. Prices range from $1,000-$4,750 per month depending on the specific deliverables.
Step by Step SEO Basics (How can I do SEO for free?)
In case you are feeling overwhelmed, here is a simple step by step guide to SEO that will help you get started:
- Make sure you have analytics tracking set up properly.
- Verify your website with Google Search Console and submit your sitemap.
- Using keyword research tools, define the most important keywords you wish to rank for.
- Match each keyword with the page on your website you want to rank for it.
- Optimize the page’s title, meta description and content based on the guidelines above.
- Get backlinks to those pages, preferably by using the target keyword as the anchor text.
- Expanding the keyword universe by creating new content:
a. Find related search terms to the keywords you are targeting (using keyword research tools)
b. Identify which of these search terms has the fewest competition, based on search volume and number of search results.
c. Write fresh and valuable content targeting those search terms, keeping in mind the guidelines discussed above. - Keep a record of how you rank for each keyword you are targeting before making any optimizations, as well as a detailed list of all the changes you made and when.
Finally, you want to monitor your ranking and analytics regularly and see which of the actions you took had the most impact. Remember, seeing results might take several weeks or even months so be patient.
How long does it take for SEO to work and is there a way to get faster Google SEO results?
Here, we have reviewed several of the backbone elements of SEO. Doing them yourself takes a great deal of time with a huge learning curve. It requires a consistent ongoing, never-ending effort along with acquired techniques and tricks-of-the-trade that can only come from actually doing SEO long enough to become an expert.
Getting results in the fastest and most efficient way is where we generally come in. We have mastered all of these backbone elements and know how to create high-quality content. We also know where and how to get valuable inbound links and deep links.
Our SEO and Content Marketing Services consistently result in increased visibility, traffic, and conversions rates. Contact us today and we can help.